Advancing Microphysiological System Testing to a Meso Scale
Our integrated multi-organ platform screening service provides superior, human-relevant data about the systemic impacts of a compound – without in vivo testing. Our technology advances microphysiological system functionality to a new level of biological relevance. Researchers can evaluate pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic profiles of test compounds with increased speed and accuracy, thanks to:
- 2D and 3D tissues and cells – offering testing at a larger scale that more closely mimics human physiology, for greater relevance compared to micro-scale MPS and organ-on-a-chip systems
- The ability to study up to three organ systems at a time
- Advanced simulated blood flow and vascularization technology to evaluate movement across biological barriers
Connect with an expert
What Sets Our System Apart From Organ on a Chip
Compared to an organ on a chip, our novel system offers greater physiological accuracy, simplicity, and affordability. Our integrated multi-organ system also offers more flexibility to meet experimental design needs, with the capacity to study up to three integrated organs, linked by a simulated vascular system. This allows for the simultaneous collection of pharmacokinetic data, including metabolite formation and organ toxicity. The plastics used in our platform – combined with our proprietary coating – enables higher logP compounds to be evaluated with less than 10% non-specific adsorption.
We rely on well-characterized cell and tissue models to represent organs on a meso scale, advancing the technology beyond the limitations posed by the small tissue masses and low fluid volumes used in MPS and organ-on-a-chip platforms. When the data obtained from our system are used to build PBPK models, the information can inform human-relevant questions of exposure and safety. When the route of exposure for a test compound is by inhalation, our platform accommodates an aerosol-generating device mounted over human reconstructed lung tissue.
Our system provides clear advantages, including:
- Human-relevant, physiologically correct data in vitro
- An understanding of compound movement in a simulated blood flow
- Preclinical data highlighting the metabolism and toxicity of a test compound
- Pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic parameters
- Information about the downstream effect of compounds on multiple organs
- PBPK modeling
How our Integrated Multi-organ System Works
In our system, each organ compartment is cultured in a mesoscale plate under optimal growth conditions for that 2D or 3D tissue or cell type. Our platform is compatible with most commercially available tissue models including our own TruVivo™, a pioneering hepatic system that provides human-relevant, reliable results.
A simulated vascular system with semipermeable membranes provides a channel for communication between organ compartments. This allows only osmotically active molecules to move in and out of the simulated blood, with no net change in fluid volumes between organ compartments.
Test material is applied to the apical surface of the intestine, lung, or skin, with movement monitored over 48 to 72 hours. The collection of multiple time point samples from all compartments, followed by Liquid Chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) analysis, allows for the development of pharmacokinetic profiles that define test article movement.
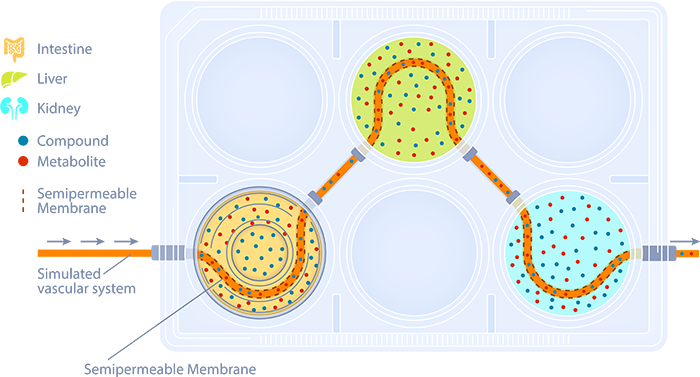
The parent material, as well as the formation of metabolites, can be tracked in this system. Cytotoxicity in each compartment can be monitored as well.
Testing Options
- Intestine-liver
- Intestine-liver-kidney
- Skin-liver
- Skin-liver-kidney
- Lung-liver
- Lung-liver-kidney
- Lung (apical)-liver-Lung (basolateral)
Guidance Every Step of the Way
We partner with every customer to offer individualized guidance. This customized approach extends from designing the study through to data analysis and reporting.
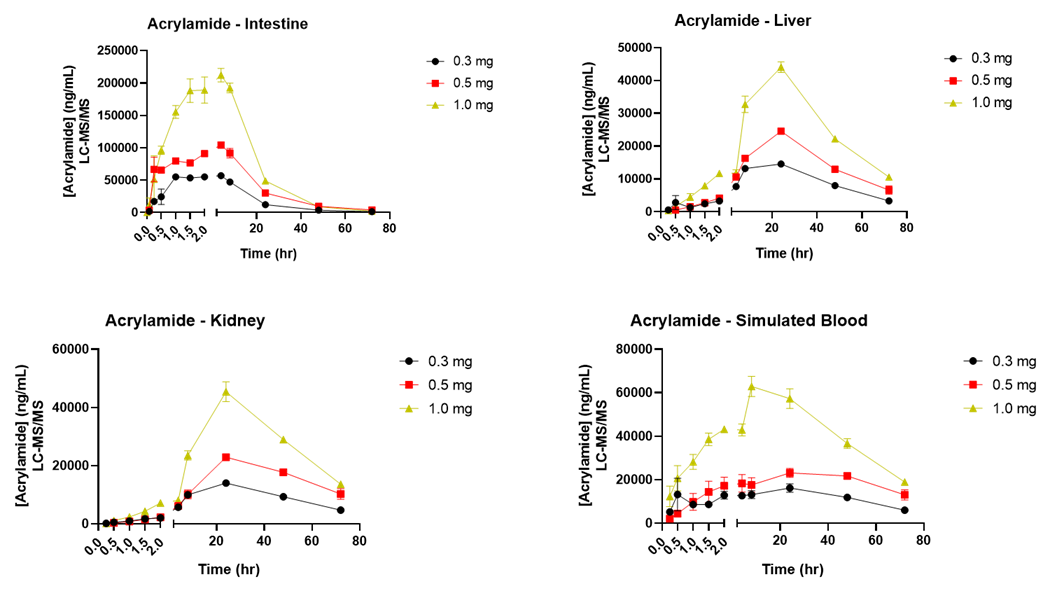
Sample Data
The example below shows kinetic data following acrylamide exposure.
Posters
Review key posters highlighting insights from projects showcasing our integrated multi-organ system.
- A Multiple Organ Integrated In Vitro Model for Studying Repeated Dose Toxicity (PDF)
- Developing Toxicity and Pharmacokinetic Models for an In Vitro Integrated Organ Platform (PDF)
- Evaluation of an Integrated Human Multi-Organ Culture Plate for Predicting Systemic Toxicity (PDF)
- In Vitro Evaluation of the Pharmacokinetics of Phenoxyethanol in the Human Dynamic Multi-Organ Plate (PDF)
